Your warehouse has inventory in stock. You’ve sold more units to customers than you can fulfill. The math is brutal: angry customers waiting for products you can’t ship.
This inventory backlog scenario plays out daily across ecommerce operations, turning profitable sales into operational nightmares. But here’s what successful companies know: inventory backlog isn’t just a fulfillment problem—it’s a predictable challenge you can measure, manage, and eliminate with the right strategies.
What you’ll learn in this guide:
- Calculate your backlog accurately using essential formulas that reveal your true fulfillment capacity
- Identify the root causes behind your specific backlog situation (demand spikes, supply issues, or internal bottlenecks)
- Implement proven strategies that companies use to eliminate backlogs and maintain smooth operations
- Prevent future backlogs through better forecasting, supplier management, and process optimization
Whether you’re dealing with seasonal demand surges, supply chain disruptions, or rapid growth challenges, these strategies will help you turn inventory backlog from a recurring crisis into a manageable part of your operations.
Key takeaways
TL;DR:
Key takeaways

Inventory backlog represents units committed to customer orders but not yet shipped from your warehouse

Excessive inventory backlog damages customer relationships, ties up working capital, and forces expensive operational workarounds

Three main factors drive most inventory backlog: high demand spikes, supply chain disruptions, and internal production process breakdowns

Calculate backlog ratios and days of inventory backlog to monitor performance and communicate realistic lead time expectations

Nine proven key strategies can dramatically reduce inventory backlog, from demand forecasting improvements to strategic 3PL partnerships
Inventory backlog: The number of units already sold or committed to customer orders but not yet shipped. Calculate it by subtracting units shipped from total units ordered. A rising inventory backlog signals that customer demand exceeds order fulfillment capacity; a shrinking inventory backlog indicates improved throughput.
Are you an ecommerce company struggling with ecommerce inventory backlog? Specializing in big and heavy fulfillment for bulky items, Red Stag Fulfillment can handle the complexities of inventory management for you. Contact our team today to learn more about our 3PL services.
What is an inventory backlog?
An inventory backlog represents unfulfilled orders that have been received and committed to but have not yet been shipped. Think of it as a queue of pending business orders where the inventory exists physically in your fulfillment center but is already “spoken for” by customer orders awaiting shipment.
When you receive customer orders, your inventory backlog grows by that number of units. If you fulfill orders the next day while receiving fewer new orders, your inventory backlog shrinks accordingly. This natural ebb and flow occurs in all business operations, but learning how to manage inventory backlog effectively prevents operational problems that destroy customer satisfaction.
Simple definition
The clearest way to understand inventory backlog is through this fundamental equation: you have products in your warehouse, customers have placed orders for those products, but the orders haven’t shipped yet. Every unit sitting in this “committed but not shipped” status contributes to your inventory backlog and affects your inventory levels.
Inventory backlog vs. order backlog vs. backorder
These terms create confusion because they’re often used interchangeably, but they represent key differences in operational challenges that require different solutions to manage effectively.
| Term | Definition | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory backlog | Units committed to orders but not shipped | Order fulfillment capacity constraint |
| Order backlog | Complete unfulfilled orders regardless of stock | Overall operational throughput issue |
| Backorders | Orders for out-of-stock inventory items | Inventory availability problem |
Understanding these key differences helps you develop targeted strategies for each scenario rather than applying generic solutions that may not address the root cause of your inventory backlog.
Why inventory backlogs happen
Three main categories of issues create inventory backlog situations. Identifying which category is driving your specific inventory backlog determines which solutions will be most essential to manage your business operations effectively.
Demand-driven causes
Sudden high demand spikes often overwhelm even well-managed inventory management systems. Viral marketing campaigns, seasonal rushes, or unexpected product popularity can create substantial inventory backlog within hours. Preorders for upcoming product releases also contribute significantly, as customer orders accumulate before inventory arrives from suppliers.
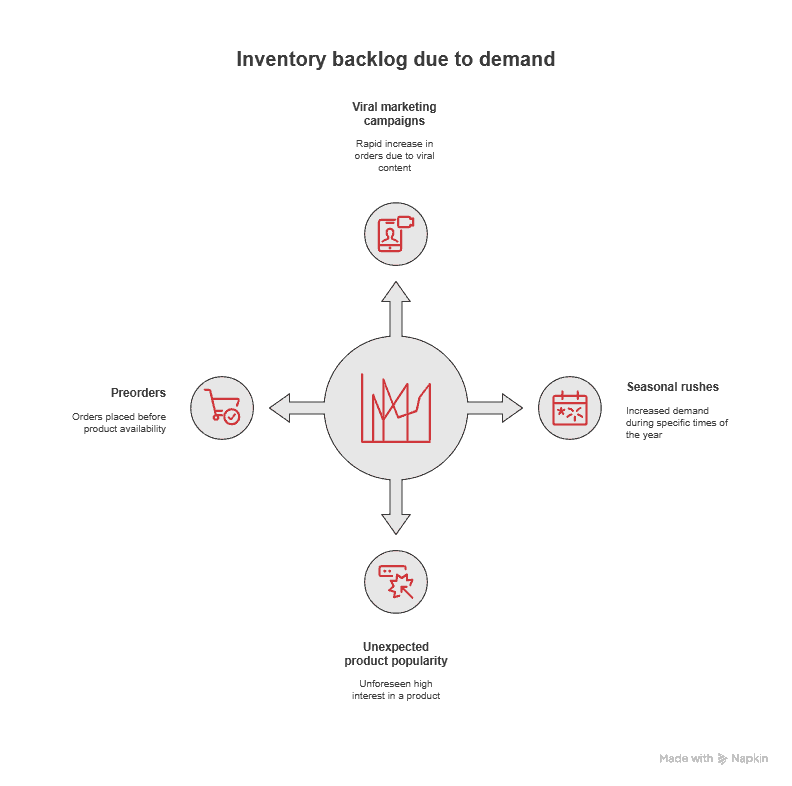
Inaccurate demand forecasting compounds these issues. When forecasts underestimate future demand, you’re left scrambling to fulfill orders with insufficient inventory levels or production capacity. When forecasts overestimate customer demand, resources get tied up in excess inventory while fast-moving products create inventory backlog.
Supply-side disruptions
Supply chain disruptions create some of the most challenging inventory backlog situations because they’re largely outside your direct control. Production delays, transportation issues, natural disasters, and geopolitical instability all slow the flow of goods from suppliers to your warehouse operations.
Manufacturing bottlenecks present particularly complex challenges. When production schedules fall behind due to equipment failures, labor shortages, or capacity constraints, the ripple effects accumulate quickly and lead to significant inventory backlog.
Internal process and data issues
Operational challenges within your own facility frequently drive inventory backlog accumulation, making them both the most frustrating and most controllable category of causes to manage.
Equipment malfunctions, staffing shortages, and inefficient production process workflows significantly slow order fulfillment. When pick rates drop due to poor warehouse layout or when packing stations become bottlenecks, customer orders pile up faster than they can be processed, creating substantial inventory backlog.
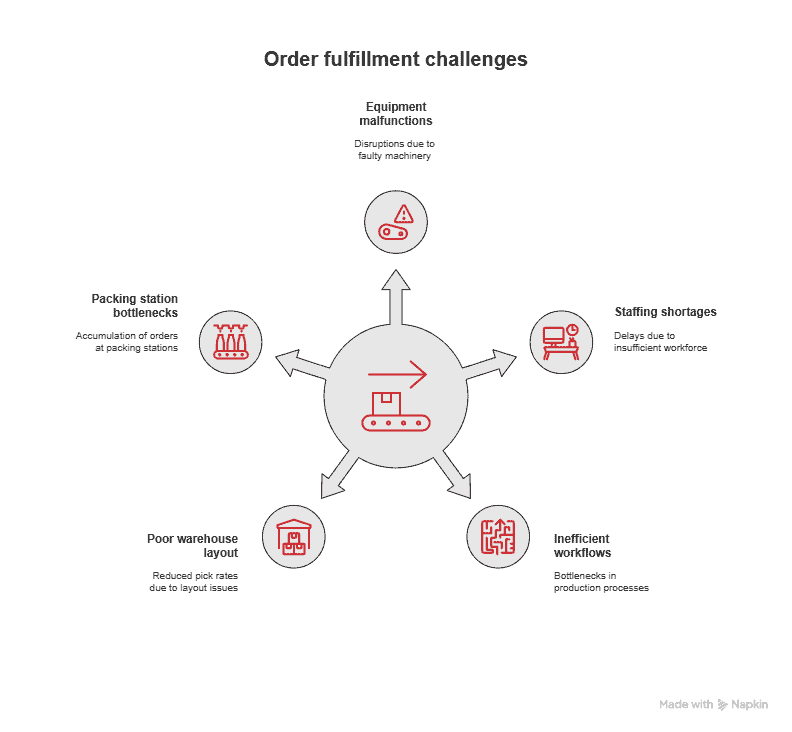
Inventory tracking errors create particularly problematic situations because they involve selling products you don’t actually have available. When your inventory system fails to update inventory levels accurately after sales, returns, or damages, you end up overselling and creating inventory backlog that can’t be resolved through faster order fulfillment alone.
How to calculate and monitor your backlog
Effective inventory backlog management starts with accurate measurement. Without clear metrics, you can’t identify trends, set realistic customer expectations, or measure improvement efforts to reduce inventory backlog.
Core backlog formula
The fundamental inventory backlog calculation provides the foundation for all other backlog metrics in your business:
Inventory Backlog = Total Committed Units – Units Already Shipped
If you have committed units across all customer orders and have shipped a portion of those units, your inventory backlog represents the difference. Perform this calculation at the SKU level for maximum accuracy, as different inventory items may have vastly different inventory backlog situations even within the same order.
Backlog ratio and days of backlog
Raw inventory backlog numbers lack context without understanding your normal order fulfillment capacity. The days of inventory backlog metric provides valuable perspective:
Days of Inventory Backlog = Current Inventory Backlog ÷ Average Daily Order Fulfillment Rate
This metric helps communicate inventory backlog status to stakeholders and set realistic customer expectations about lead time for shipping.
The backlog ratio offers another useful perspective:
Backlog Ratio = Current Inventory Backlog ÷ Total Available Inventory
PRO TIP: Track both unit-level and order-level backlogs separately. A high unit inventory backlog with low order backlog might indicate large wholesale orders, while high order backlog with moderate unit inventory backlog suggests many small consumer orders requiring different order fulfillment strategies.
Excessive inventory backlog creates cascading problems that extend far beyond delayed shipments. Understanding these hidden costs helps justify the investment required to implement proper inventory management systems to control and manage inventory backlog effectively.
Customer experience impact
Extended lead time delays directly damage customer satisfaction in ways that compound over time. Today’s customers expect fast shipping and clear communication about order status. When inventory backlog creates uncertainty about delivery timelines, customers lose confidence in your ability to meet customer demand for future orders.
One frustrated customer doesn’t just represent one lost sale—they represent lost lifetime value, negative word-of-mouth marketing, and potentially damaging online reviews that influence future customers and your business reputation.
Working capital and cash-flow drain
Inventory backlog ties up working capital without generating immediate revenue returns. Every unit committed to an unfulfilled order represents cash invested in inventory that can’t be reinvested in growth activities or used to meet other financial obligations for your business.
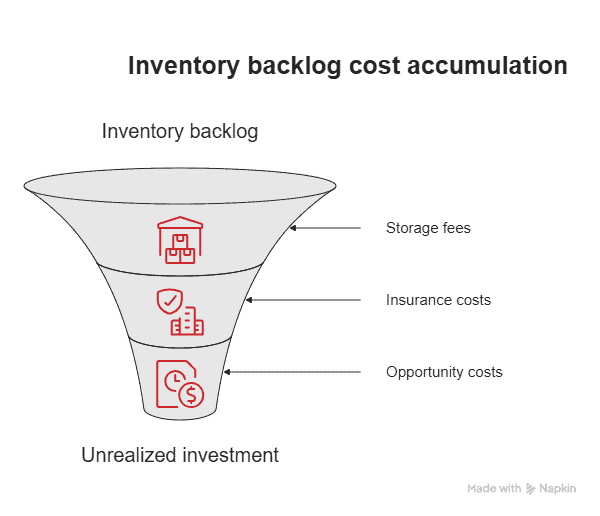
Storage fees, insurance costs, and opportunity costs accumulate while your investment remains unrealized. These carrying costs become particularly painful during extended inventory backlog periods when the same inventory generates costs for weeks or months without producing revenue.
Operational stress and overtime costs
Inventory backlog pressure forces business operations teams into reactive mode, creating expensive operational patterns that become difficult to break. Overtime costs increase as teams work extended hours to clear accumulated orders, and rushed order fulfillment leads to errors that create additional customer service issues.
This operational stress impacts employee morale and retention, creating long-term challenges that extend beyond the immediate inventory backlog situation and affect your ability to manage future demand effectively.
When a backlog can be good
Not all inventory backlog represents operational failures. A well managed inventory backlog often indicates strong product demand and provides valuable business insights that help optimize operations and growth planning.
Consistent moderate inventory backlog suggests popular products without overwhelming operational capacity. Inventory backlog also provides buffer time for production planning and inventory management, offering visibility into committed orders that helps optimize purchasing decisions and production schedules to meet customer needs.
NOTE: The key is maintaining inventory backlog within manageable ranges that don’t compromise customer satisfaction or operational efficiency. Most successful operations target inventory backlog levels that represent no more than a few days of normal order fulfillment volume.
9 proven strategies to reduce or avoid backlogs
Successful inventory backlog management requires systematic approaches that address root causes rather than just symptoms. These nine key strategies have proven effective across different industries and business models to manage inventory backlog and improve efficiency.
Tight demand forecasting
01
Implementing more accurate demand forecasting reduces the likelihood of stock shortages that create inventory backlog. Modern demand sensing technologies combine historical sales data, market trends, and external factors to create more reliable forecasts. Machine learning algorithms excel at identifying complex patterns in customer demand data that traditional forecasting methods miss.

A robust inventory management system with advanced demand forecasting capabilities helps you anticipate future demand and maintain optimal inventory levels. This proactive approach prevents situations where customer demand exceeds available inventory, reducing the risk of inventory backlog formation.
Reorder point optimization and safety stock
02
Strategic reorder point calculations ensure timely restocking occurs before stock shortages create inventory backlog. The reorder point formula provides a starting framework:
Reorder Point = (Average Daily Demand × Lead Time) + Safety Stock
Consider demand variability and supplier reliability when setting safety stock levels. Having enough inventory on hand prevents stockouts that lead to inventory backlog, while avoiding excess inventory that ties up working capital unnecessarily.
Supplier collaboration and dual sourcing
03
Strengthening supplier relationships through regular monitoring and collaborative planning sessions reduces supply chain disruption risks. Dual sourcing strategies reduce dependence on single suppliers and provide alternatives during unforeseen events or logistical issues.
Developing strong supplier relationships ensures more reliable lead time commitments and better communication during potential supply chain management challenges. This proactive approach helps maintain steady inventory flow and prevents supply-side inventory backlog.
Warehouse slotting and pick-pack automation
04
Optimizing warehouse layout significantly impacts order fulfillment speed and capacity. Placing high-velocity inventory items in easily accessible locations reduces pick times and increases daily throughput capacity to manage inventory backlog more effectively.
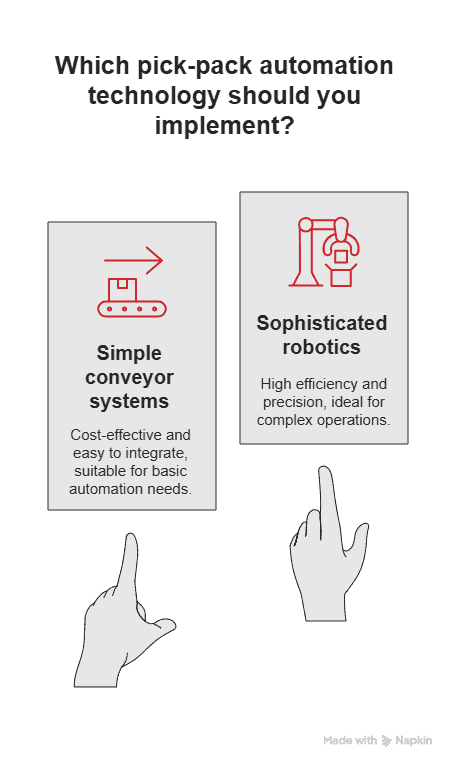
Pick-pack automation technologies range from simple conveyor systems to sophisticated robotics that improve efficiency in your fulfillment operations. These investments help you process customer orders faster and reduce the time inventory spends in backlog status.
Lean production scheduling
05
Applying lean manufacturing principles to order fulfillment operations minimizes waste and optimizes throughput. Finite capacity planning ensures production and order fulfillment schedules align with actual capacity constraints rather than optimistic projections.
This crucial approach to production process management helps prevent bottlenecks that create inventory backlog. By synchronizing production with demand and maintaining steady workflow, you can better control inventory levels and meet customer expectations.
Preorder and back-in-stock communication tactics
06
Proactive customer communication manages expectations and reduces customer frustration during inventory backlog periods. Automated notification systems for back-in-stock alerts and order status updates keep customers informed without requiring manual intervention from your business.
Clear communication about lead time expectations helps maintain customer relationships even when inventory backlog occurs. Providing regular monitoring updates and realistic delivery timelines builds trust and reduces the negative impact of delayed shipments.
Real-time inventory visibility tools
07
Deploying a comprehensive inventory management system with warehouse management systems (WMS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms provides real time view of inventory across all locations. This visibility enables faster decision-making and prevents overselling situations that create artificial inventory backlog.
Real-time inventory tracking updates prevent the overselling that creates problematic inventory backlog situations. Having accurate, up-to-date information about stock levels allows you to make informed decisions about order fulfillment and manage customer expectations appropriately.
3PL partnerships
08
Working with experienced third-party logistics providers offers scalable order fulfillment capacity during peak periods or rapid growth phases. Established 3PLs have systems, processes, and capacity that can absorb high demand spikes without creating inventory backlog.
These logistics partnerships provide access to advanced inventory management systems and ecommerce fulfillment expertise that can help you manage inventory backlog more effectively. Working with experienced 3PL providers gives you flexibility to scale operations without investing in additional warehouse infrastructure.
When evaluating potential partners, understanding how to choose a 3PL ensures you select a provider with the capabilities and experience to handle your specific inventory management challenges effectively.
Continuous improvement programs
09
Implementing Kaizen methodologies systematically identifies and eliminates order fulfillment inefficiencies before they create inventory backlog problems. Establishing sales and operations planning (S&OP) processes aligns demand forecasts with operational capacity, preventing the mismatches that create inventory backlog.
Regular monitoring of key performance indicators helps you identify trends and implement contingency plan measures before small issues become major inventory backlog problems. This essential approach to business operations ensures continuous improvement in your ability to manage inventory backlog and meet customer demand.
Frequently asked questions
What does inventory backlog mean?
Inventory backlog refers to customer orders that have been received and committed to but not yet shipped from your warehouse, representing units awaiting fulfillment.
Is backlog good or bad for a company?
Moderate inventory backlog indicates healthy customer demand, but excessive inventory backlog creates customer satisfaction issues, ties up working capital, and strains business operations resources.
How do you calculate backlog inventory days?
Divide your current inventory backlog by your average daily order fulfillment rate to determine how many days of normal operations your inventory backlog represents.
What causes inventory backlog in ecommerce?
The three main causes are high demand spikes that exceed order fulfillment capacity, supply chain disruptions that delay inventory replenishment to maintain adequate inventory levels, and internal operational issues that slow the order fulfillment process.
What is the difference between backlog and backorder?
Inventory backlog includes all unfulfilled orders regardless of inventory status, while backorders specifically refer to orders for out-of-stock products that require timely restocking.
How does inventory backlog affect financial statements?
Inventory backlog ties up working capital, impacts cash flow, and can affect inventory turnover ratios and revenue recognition timing on financial statements for your business.

