Dropshipping is a low-entry way for almost anyone to start an ecommerce business. Suppliers handle fulfillment and logistics, so you can focus on sales, customer service, and growth.
In this dropshipping guide, you’ll learn what it takes to get started and build a successful ecommerce business.
TL;DR:
What is dropshipping?

Dropshipping is a business model where you sell products without holding inventory—suppliers ship directly to your customers.

The main benefits include low startup costs, minimal risk, and the ability to focus on marketing rather than logistics.

Challenges include lower profit margins, limited control over product quality and shipping, and potential customer service complications.

Success requires careful supplier selection, excellent customer service, smart niche selection, and strategic product pricing.
What is dropshipping?
Dropshipping is a type of ecommerce business model where you sell products without holding inventory. When a customer places an order on your website, the order details are forwarded to your supplier who ships the product directly to your customer. You never physically handle the product.
This model is attractive to some entrepreneurs because you don’t have to buy stock upfront or manage storage like with traditional ecommerce. Instead, you act as a middleman and store manager, listing products for sale on your website or other digital channels.
When a customer places an order, you pay your supplier for the items in the order, and the supplier sends the items directly to your customer. You never actually handle any items or packages.
You can sell a wide variety of products with a dropshipping model, just like you can sell products across multiple categories on traditional ecommerce stores. The flexibility and low cash requirements reduce the risk of launching new online stores and introducing new products.
How does a dropshipping business work?
Dropshipping businesses are unique because of how you fulfill orders. With a traditional ecommerce business model, your team fulfills orders, or you partner with a third-party logistics (3PL) provider to fulfill orders on your behalf.
A dropshipping business takes the steps to fulfillment, also known as the order lifecycle, off your plate entirely. Here’s how it works.
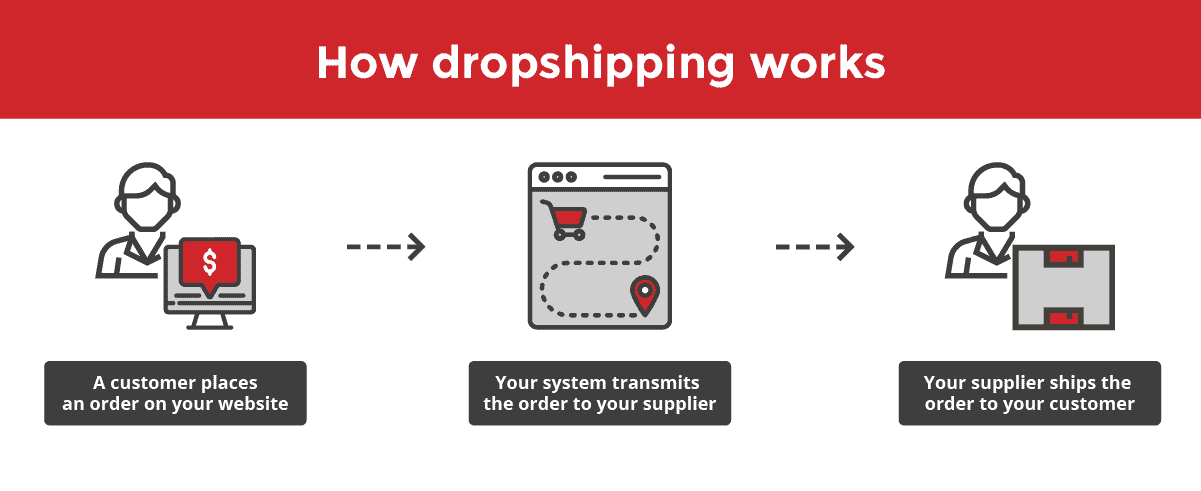
A customer places an order
The full order life cycle begins when a customer visits your online store and places an order. At this stage, your dropshipping transaction is like any ecommerce sale. The customer has paid for their items and is waiting to receive them.
You forward the order to your supplier
Instead of fulfilling the order from inventory you already have, with dropshipping, you send the order to your supplier. You can usually automate this process through your online store platform.
Your supplier fulfills the order
Your dropshipping supplier picks or produces products from their own inventory and packages the items for shipping to your customer. They take care of the shipping, although you may pay them a shipping fee that depends on your customer’s location.
The customer receives the order
Your customer receives the dropshipped items from a final-mile logistics provider, like UPS, FedEx, or DHL. Once the customer receives their package, the order lifecycle is usually complete, unless they have an issue with the item.
Drop shipping versus other types of ecommerce
Dropshipping represents a shift in roles and responsibilities compared to typical ecommerce or brick-and-mortar retail store models. The main differences are who holds inventory and who fulfills orders.
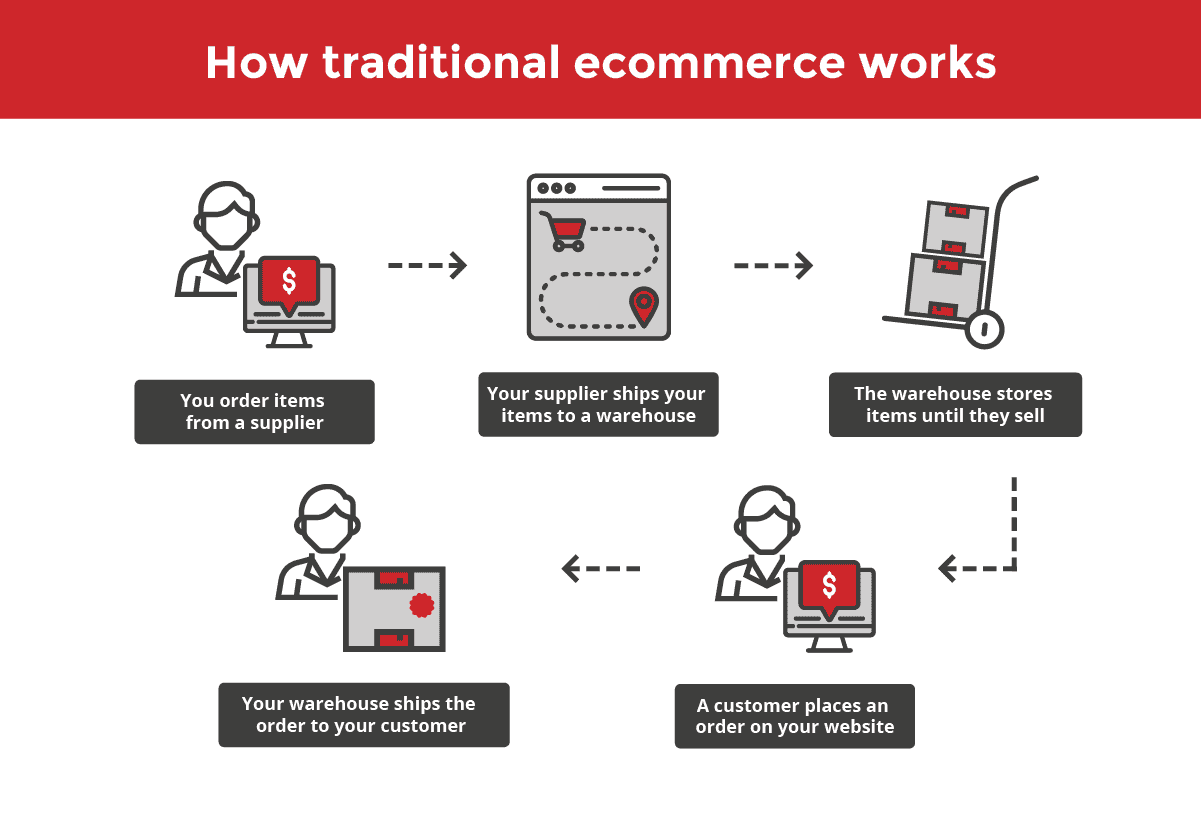
In traditional ecommerce, the store owner or brand has a lot more responsibility:

Buying inventory from suppliers

Paying for shipping from the supplier

Paying to store inventory in a warehouse

Managing inventory levels for profitability

Packing and shipping items to customers
But if you know how to dropship, you can shift your attention to growth activities.

Identifying customer personas and ideal customer profiles (ICPs)

Forecasting and demand planning to align with what customers want

Product sourcing and finding new dropship partners to help you grow

Marketing and advertising, including strategy and content production
Traditional ecommerce stores need to allocate resources to these activities, too, but leaders risk getting lost in the weeds. Managing fulfillment and growth is a lot of work. Dropshipping fulfillment makes it easier and more realistic for new business owners.
How to get started with dropshipping
Learning to start a dropshipping business is relatively simple compared to other retail models. You can do these steps in sequence or work on them at the same time.
Perform market research
01
Kickstart your dropshipping store with thorough market research. This involves evaluating market demand for specific products, competition from other stores or marketplaces, and potential profit margins across different product niches.
Use free search tools like Google Trends to gauge demand signals and determine market viability.
Choose a platform for your online store
02
Selecting the right platform for your ecommerce store can help streamline operations once you launch. Explore popular platforms like Shopify, BigCommerce, or WooCommerce. These platforms serve as the foundation for your online store, providing essential tools and features for managing your dropshipping business.
Source drop shippers
03
Identify reliable drop shipping companies by checking your ecommerce platform’s app marketplace or browsing dropshipping marketplaces and directories.
During this discovery phase, assess factors such as pricing, minimum order quantities (MOQs), shipping times, and return policies. Confirm that dropshipping suppliers can connect with your online store’s platform for automated order processing.
Set up your online store
04
Once you’ve selected your platform and dropshipping suppliers, it’s time to set up your online store.

Begin by choosing a memorable and relevant domain name that reflects your brand identity.

Design your page layouts, including product category and individual product pages, using themes or templates provided by your ecommerce platform.

Populate your store with products and their variants, such as colors and sizes. Include compelling marketing descriptions and images.

Configure payment processing using your platform’s shopping cart builder, offering multiple payment options to accommodate customer preferences.

Before launching your store, test its functionality across various devices to provide a seamless customer experience.
Develop your marketing
05
With your store set up, shift your focus to launching your marketing initiatives.

Develop a tactical plan outlining your chosen channels, such as social media, advertising campaigns, and partnerships with affiliates or influencers.

Create engaging content, including images and copywriting, and establish clear timelines and milestones for implementation and measurement.

Publish targeted content to drive traffic to your store. Experiment with organic and paid content to find what works for you.
Track and analyze data
06
To optimize your strategies, continuously monitor and analyze key metrics such as website traffic, sales data, and marketing performance.
By tracking your progress and identifying areas for improvement, you can make informed decisions that enhance the overall success of your dropshipping business.
What products can I drop ship?
You can drop ship merchandise across several product categories. If there’s a market for it and you can find a supplier, you can experiment with adding it to your store.
Ideal dropshipping products have unique selling propositions or hooks that appeal to a broad audience:

Apparel and accessories

Home goods

Pet care accessories

Home exercise equipment
PRO TIP: Consider avoiding fragile or complex items with many parts when starting your dropshipping business. You have limited control over production quality, and if items break, you’re responsible for fixing the situation with customers.
You can also offer customizable products. For instance, you could feature apparel items with your designs. Some dropshipping suppliers can print them on-demand across different SKUs and variants, like T-shirts, tanks, and hoodies in different colors.
NOTE: Even though you’re not the one producing items, you still have to comply with relevant product laws. Stringent U.S. intellectual property laws prohibit the sale of counterfeit goods, and products made with forced labor are off-limits. Most dropshipping partners present minimal risk, but do your research to be sure.
Dropship fulfillment pros and cons
As you learn how to dropship, you’ll discover ways to lean into opportunities and minimize risks, considerations, and constraints. Understanding these factors can help you develop strong strategies, so your dropshipping business succeeds over time.
Dropshipping pros
Many people who want to start a business look to the dropshipping business model for its relatively low barriers to entry. Low cash requirements make it a more accessible option than other types of retail.
Lower startup investment
Startup costs are significantly reduced without the need to invest in inventory. If you’re a single business just getting started, you can limit your personal investment. If you’re an established entrepreneur seeking partners, you may be able to control a larger share of your new business because you don’t need as much money from others.
You also don’t have to invest in fulfillment infrastructure because your dropshipping supplier takes care of those parts of the business.
This includes:

Warehouse rental or ownership

Inventory storage or carrying costs

Boxes, infill, and other packing materials

Warehouse labor for picking and packing

Transportation to and from warehouses
The lower investment requirements make dropshipping attractive to many entrepreneurs. In times of economic uncertainty, it can make the difference between being able to start a business or not.
Easier business management
Dropshipping requires less specialized knowledge than other kinds of retail, too. With fulfillment offloaded to suppliers, you can focus on the digital and customer sides of the business model:

Product-market fit

Brand development

Online store optimization

Marketing and advertising
These reduced responsibilities let you start and scale your business without worrying about hiring people in-house to handle fulfillment. As you grow, you may want to add more products or experiment with buying inventory upfront, but it’s easier to learn as you go with a dropshipping business model.
Dropshipping cons
Like any business model, dropshipping has risks and constraints. Some of these are outside your control, but there are ways to offset their impact. As your business grows, you may find it’s easier to navigate challenges, especially if you’re aware of them before you get started.

Lower profit potential
Dropshipping businesses may make less money than traditional ecommerce or brick-and-mortar retailers. That’s because of your margins.
Your cost of goods sold will almost always be higher when you partner with a dropshipper than when you buy inventory before you sell it. Dropshipping suppliers don’t benefit from volume sales the way traditional wholesalers do. This means you don’t benefit from volume discounts. Negotiating discounts is a common way to expand profit margins with other retail models.
Key Takeaway: By shifting more business activities to the dropshipping supplier, you’re also shifting cost to serve back to them. Things like inventory management and fulfillment can be cash-intensive. With more costs to cover, your supplier builds them into your price.
You also lose control over landed cost to dropshipping suppliers or other warehouses and customers. Landed cost is the total cost of transporting goods from manufacturers, including overseas. A key way retailers squeeze more profit out of supply chains is by optimizing landed cost. There are a number of ways to do this:

Allocating labor for cost efficiency can reduce expenses greatly. Some companies assign high-priority tasks to skilled workers and automate repetitive or low-value tasks.

Comparing packaging options helps you find lighter, less expensive materials that still protect products from damages. At scale, even small changes can make a difference.

Negotiating shipping rates can help save large amounts of money when shipping from manufacturers to suppliers or from suppliers to customers.
But when you aren’t in charge of fulfillment, you aren’t in charge of landed cost. Dropshipping suppliers are unlikely to share this information with other online stores. When they optimize, they reap the benefits, not you.
Less control over product availability
Product availability can be another issue for some dropship businesses. This can take two forms:

Limited products based on your dropshipping supplier’s inventory

No control over ongoing availability of existing products
You may find that sourcing, or finding products to sell, is more challenging than you expected. Products may not seem that unique compared to your competitors. In this case, customization or personalization opportunities can offset this constraint. Make basic products feel like your own with branded designs.
Challenges with ongoing availability may be harder to hedge. Delays or stockouts can lead to lower customer satisfaction levels.
WARNING: Without visibility into your supplier’s inventory levels, you have no way to know if they’re running low on products. This can lead to stockout messages on your store, lost sales opportunities, and decreased customer satisfaction.
Gaps can lead to stockout messages on your store, lost sales opportunities, and decreased customer satisfaction. This is where things can snowball, too, because keeping customers happy is directly tied to customer acquisition costs, or the total you pay to earn a new customer. If you lose existing customers, you have to find new ones and that usually requires cash.
There’s another way stockouts can get sticky. Depending on the lag between customer orders and dropshipping supplier fulfillment times, you may have to issue refunds. You’d be responsible for processing the refund, plus any third-party fees associated with the transactions, so you even end up losing money.
Slower customer deliveries
Delivery times can be a harsh reality for dropship store owners. Orders may not be fulfilled for up to a week or longer and then they still have to ship.
For traditional ecommerce stores, pick and pack usually starts within minutes or hours of orders. Inventory is available on shelves and moves through warehouses to carriers for final-mile delivery.
But with dropshipping, items may not be produced until customer orders are placed and transmitted to suppliers. If products require production or customization after ordering, lead times could be even longer. Sometimes, speed can’t be a priority because it’s costly and dropshipping suppliers’ margins are too slim to justify it.
Limited control over customer satisfaction
Beyond stockouts and slow deliveries, dropshipping can present additional risks to customer satisfaction. You don’t have much control over or visibility into issues.
If something goes wrong, you may need to coordinate with your dropshipping supplier. You could find yourself trying to resolve issues blind. Customers may find this disappointing and fail to shop with you again or leave you bad reviews.
Some companies just replace items because it’s faster and easier, but this still incurs costs and hits your profit margins. If it happens frequently and you don’t have a good way of tracking it, it could distort your SKU analysis, making certain items look less attractive to customers when the problem is really your dropshipping supplier.
Lower scalability
Some of the risks of dropshipping may constrain growth as a whole, especially when it comes to scalability.
Typically, scalability might be considered an opportunity for any ecommerce business. But with dropshipping, you don’t control the necessary factors, like product availability and delivery speeds. Without this control, you can’t gauge predictability—and predictability is vital to growth.
Technically, you could invest in scaling your SKU array through a single channel, such as offering more products or variants on your website. You could also scale your marketing across various platforms, like repurposing your Facebook ads for Instagram.
But without full control over product quality and availability, there’s a higher risk of sunk costs or losses.
Tips for dropshipping success
Learning how to do drop shipping in a way that works for you may take some trial and error. Increase your chances of success and sidestep certain risks by following industry tips and best practices.
Choose the right product category

Find a niche you enjoy. When you can relate to your customers, you’ll be more motivated to research and market products.

Research market trends. Look for products with growing demand and low competition.

Consider product size and weight. Shipping costs can impact profitability, especially for large or bulky items.
Find reliable dropshipping suppliers

Research supplier reputation. Check online reviews, forums, and industry resources. Your online store platform’s app marketplace might include ratings and reviews for dropshipping suppliers.

Request samples. Make sure product quality aligns with your brand image and won’t result in dissatisfied customers.

Compare shipping costs and speed. Cost versus speed is a common challenge for any ecommerce company, but dropshipping has longer lead times, so it’s even more important to find the right balance.
Calculate pricing and profitability

Factor in all costs. Dropshipping is attractive for its low upfront cash requirements, but that means margins are slim. Tally up supplier costs, shipping fees, and other costs to serve, including platform charges and marketing costs.

Research competitor pricing. Traditional ecommerce stores and marketplaces have optimized infrastructure that allows them to offer the most attractive prices.

Offer promotions to earn new and loyal customers. Sales, discounts, bundles, and upsells can increase your order values.
Offer excellent customer service

Provide clear communication. Dropshipping delivery times may seem long to customers, but transparency on timing can offset the risk of disappointment.

Respond quickly to customers. Your online store platform or other communication tools may let you automate responses, so customers know you received their message. Follow up promptly so they aren’t left hanging.

Go the extra mile to provide satisfaction. With dropshipping, you have less control over product quality, availability, damages, and other exceptions. Offset these risks with excellent customer service. Some stores replace products, no questions asked.
Test new products

Start with a few products. Gauge customer interest before expanding your inventory to limit your investment of time, effort, and marketing or other upfront costs.

Align launches with demand. Consider seasonal or limited-edition collections to give customers a reason to come back to your online business.

Promote new products. Run limited-time promotions to test the waters and then lean into pricing and expansion.

Pivot quickly. Discontinue products that aren’t performing well and replace them with new offers based on data and insights.
Common challenges and solutions
How do I find reliable dropshipping services?
Research is key. Directories and marketplaces like AliExpress, SaleHoo, Sprocket, and others can provide businesses by category or other filters. Read reviews and customer stories to assess dropshipping suppliers’ online reputations. Order samples to test reliability and quality.
How do I handle returns?
Returns can work differently between traditional ecommerce and dropshipping. When you have a traditional ecommerce business, customers can send items directly to your warehouse or your 3PL for returns processing.
With dropshipping, you could have to manage multiple scenarios:

Some dropshipping suppliers may not accept returns, especially for customizations.

Your dropshipping partners may have different rules about what they’ll accept.

You may have to create multiple returns workflows across partners, which means customers could have to return two items from the same order to two different places.
PRO TIP: Consider calculating the cost of replacing items or providing refunds based on your data and working this cost into your pricing. If your margins allow, this will let you provide a more generous return policy compared to other dropshipping companies.
You might also decide not to accept returns, but this could lead to customer disappointment. One way around this is to calculate the cost of replacing items or providing refunds based on your data and work the cost into pricing. If your margins allow, this will let you provide a more generous return policy, especially compared to other dropshipping companies.
You may also need to partner with a 3PL if you sell using a dropship model on Amazon. That’s because Amazon processes returns if you use Fulfillment by Amazon, but not if you use dropshipping.
In this case, you could give customers a shipping label to return items to a 3PL partner that can help coordinate from there.
Can I do anything about slower deliveries?
Dropshipping relies on suppliers for fulfillment and shipping, so you don’t have complete control over timing.
Mitigate risks to customer satisfaction with the following tips:

Choose suppliers with faster shipping options

Communicate expected delivery times clearly to customers

Offering tracking information to keep them updated

Provide discounts for next time to make up for delayed deliveries
How can I earn customer loyalty?
You can earn customer loyalty in similar ways to other retail or service-oriented businesses:

Quality products

Personalized communication

Sales, promotions, and other incentives

Answering questions quickly

Responding to feedback and reviews
When you have a dropshipping store, these factors may be more important. Since you have tighter profit margins, you don’t want to alienate customers. Fast, consistent customer service can help keep them interested in your store.
Drop ship fulfillment alternatives
You can also select other ecommerce models for your new business or to supplement your drop ship fulfillment model.
Retail arbitrage
Retail arbitrage involves selling items for higher prices on your site or other platforms that can support the price increase. It’s more manual than dropshipping companies and other business models. This means it’s not as scalable but can be lucrative in certain scenarios.
This model is best suited for niche product categories or products with dedicated fan communities, such as sneakerheads or celebrity fashion drops.
Additionally, it works well for very low-margin items where price sensitivity is minimal. For example, a customer might be willing to pay $3 for an item anyone could buy for $1. The difference is negligible for the customer, given the convenience or uniqueness of the product, but the margins can add up for you. Achieving volume this way isn’t always a sure bet, though.
Private label fulfillment
Private label fulfillment offers a middle ground between dropshipping and traditional ecommerce retail, allowing you to customize or differentiate products with your private label.
This approach lets you invest in lower quantities of products while maintaining control over quality, process, and profitability. And because you integrate your website with a fulfillment center, rather than dropshipper that sells across multiple partners, you may have greater visibility. This could let you see more on inventory levels, fulfillment stages of orders, and other supply chain data.
The increased visibility can also help you resolve issues and make optimizations promptly, providing more opportunities for brand differentiation and loyalty.
Traditional ecommerce
Traditional ecommerce involves the full capital investment typical of retail operations, where you purchase inventory upfront and manage fulfillment directly. Unlike dropshipping or retail arbitrage, traditional ecommerce requires you to hold inventory, which can be both a financial commitment and a logistical challenge. However, it offers complete control over product selection, pricing, branding, and customer experience.
With traditional ecommerce, you have the flexibility to customize your website and curate a unique product assortment to build a loyal customer base. You manage your inventory levels, shipping processes, and customer service in-house or with a 3PL, giving you full autonomy over every aspect of your business operations.
While it requires more upfront investment and ongoing management, traditional ecommerce provides the opportunity for higher margins, greater brand control, and long-term sustainability.
If you’d like to learn more about how Red Stag Fulfillment can help you with dropshipping returns or other fulfillment models, reach out.
