Successful ecommerce businesses all have one thing in common: terrific ecommerce fulfillment.
You can have the best product in the world, an inviting website, and a sales funnel that slides your customers quickly to the checkout, but if your ecommerce logistics don’t run smoothly, your web-based business will be all splash and no cash. Fulfillment logistics may not be the thing that gets you excited about your online business, but it’s a crucial factor contributing to the success of your online store.
Fulfillment and shipping costs can be a drag on your business, driving up prices and eating into your profit margins. Late deliveries, fulfillment errors, and failure to live up to the level of service you promise can alienate customers.
Predictable and accurate ecommerce fulfillment is vital to customer satisfaction and saving time and money. A well-executed national fulfillment strategy is an engine of business growth that fuels expansion for many of the top ecommerce brands.
You don’t have to process orders yourself (in fact, it’s often better to outsource order logistics & utilize ecommerce fulfillment services), but understanding ecommerce warehousing and fulfillment processes will help you build a robust foundation for a thriving ecommerce operation.

What is ecommerce fulfillment?
Ecommerce fulfillment is the segment of your supply chain that receives bulk goods, stores SKUs in a warehouse, picks and packs orders, and delivers products to your customers. Your online order fulfillment processes include the following:
- Getting products onto ecommerce fulfillment center shelves
- Placing SKUs into inventory
- Picking and packing orders
- Order delivery
- Managing returns
We discuss all these elements and more in detail below.

How do you fulfill an ecommerce order?
Every ecommerce business needs a fulfillment process. For the smallest online sellers, that might mean a few shelves of product in the garage, picking and packing orders yourself, and taking boxes to the Post Office, FedEx, or UPS.
For larger enterprises, ecommerce fulfillment starts with a full container or truckload shipment or pallets of stock delivered to the fulfillment warehouse. Workers add your products to the warehouse management system (WMS) and place them on shelves.
When a customer places an order, integration between your ecommerce platform or order management software delivers the order to the WMS almost immediately. The order generates a pick list, which a picker uses to pull items to fill the order. Then, a packer secures the products in a box for shipping, and the 3PL hands the package off to a carrier for delivery.
The ecommerce fulfillment process
The ecommerce fulfillment process has several distinct steps (each with many sub-steps). Here’s a breakdown of the main components of fulfillment logistics.

Receiving
Fulfillment warehouses have dedicated receiving bays where trucks arrive to offload clients’ products. To keep things running smoothly, you should provide an advance shipping notice (ASN) telling the warehouse the contents of your shipment and when it will arrive. The warehouse will ensure that workers are available to unload your merchandise and log it into the WMS quickly. A 3PL best practice is to check the shipment’s contents against the ASN. Receiving is the best place to find goods damaged in transit or SKU discrepancies. Thorough inbound processes prevent inventory errors.
Many ecommerce warehouses fall short in receiving. When pallets sit on a loading dock, your products aren’t in inventory, and you may miss out on sales. Look for an online order fulfillment services provider that places stock into inventory within one to two days of receiving it. The 3PL should also provide accurate, up-to-date inventory data to supercharge your inventory management.

Warehousing
Warehousing ecommerce products involves managing stock within a dedicated space. Although one of the warehouse functions is storage, it’s not a dusty library of rarely moved products. Instead, a fulfillment warehouse is a dynamic place where goods move in and out, turning over quickly.
Storage
Fulfillment warehouses have well-defined systems for putting products on the shelves. Aisles and shelves are labeled, and each SKU has its own shelf location, mapped in the WMS. When an order comes in, the system generates a picklist with each SKU’s aisle and shelf location. Shelves are labeled and bar-coded so pickers can use scanners to verify they’re in the correct area to pick an item for an order.
Warehouses organize storage in several different ways, but common strategies include:
- Separate products that could get mixed up. If the warehouse stocks blue shirts in multiple sizes, it won’t line them up in a row like a retail store would because it’s too easy for a picker to take a small instead of a medium without realizing it. A chaotic storage system makes picking easier.
- Place items with the highest sales volume closest to the packing station. Another goal of warehouse storage is to support efficient order fulfillment. Placing high-volume SKUs close to the packing area means the picker doesn’t have to walk far to drop completed orders.
- Organize stock into zones. Many warehouses use wave or zone picking, where each picker operates within a specific zone, filling partial orders and passing them off to a picker in the next zone.
Another critical element of warehouse storage is security. State-of-the-art warehouses have robust security systems, including camera coverage of the entire space and 24/7 security.
Inventory management
Inventory management is a hot topic in ecommerce because it’s critical to growing a business. Keeping inventory levels on hand to meet demand without tying up more cash than necessary requires complex calculations and continuous adjustment. Keeping your inventory lean also reduces inventory storage costs.
For a 3PL, inventory management means ensuring that the merchandise it stores for its clients is secure, safe, handled properly, and slotted correctly to facilitate efficient picking. Many fulfillment companies also assist clients with supply chain inventory management.
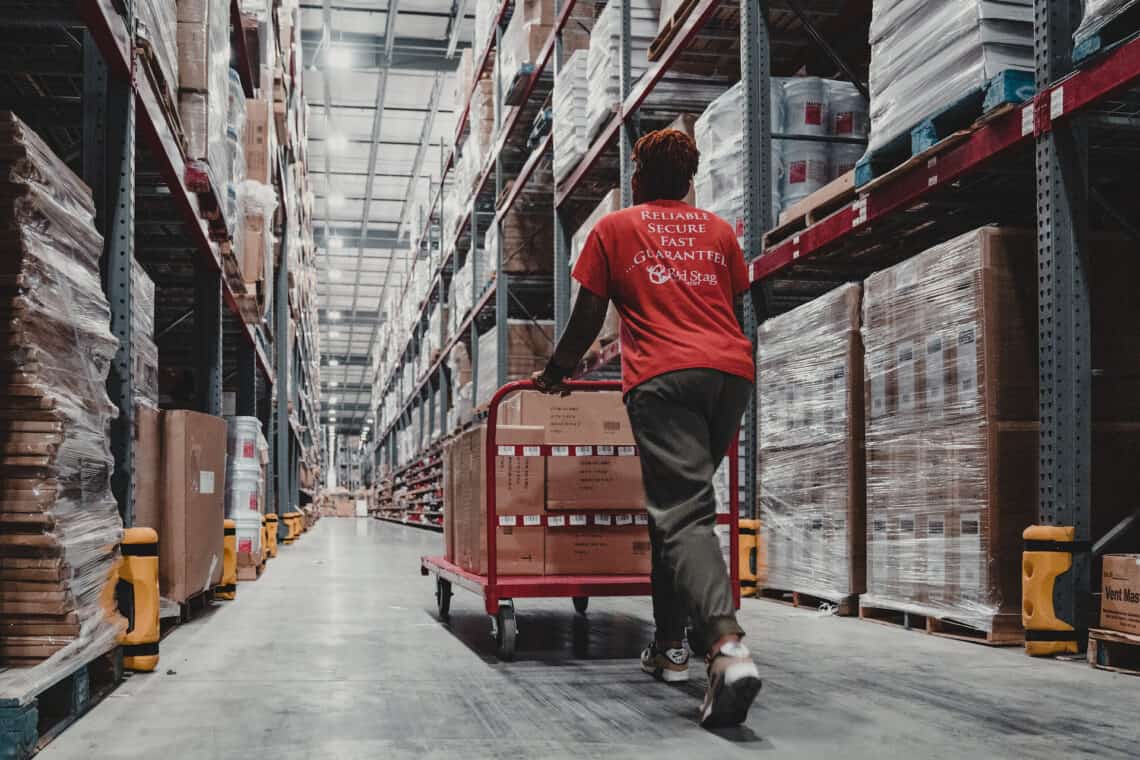

Picking and packing
When a customer places an order, your software sends it to the WMS, which generates a pick list or packing slip. Pickers use the lists to place all items for a single order into the same bin. Those bins go to the packing station, where packers find the right box size, add infill to keep items from moving during shipping, seal the box, and apply the shipping label.
There are several different methods of picking. Small warehouses or in-house fulfillment operations may pick each order individually. In more extensive operations, the WMS groups orders with the same SKUs or in the same warehouse zone, and pickers process many orders at once.
A best practice for order processing is to pick and pack customer orders the same day the customer places them or the next day at the latest. Pick and pack backlogs feel like shipping delays to the person who places the order and make it harder to meet customer expectations for fast order shipping times.
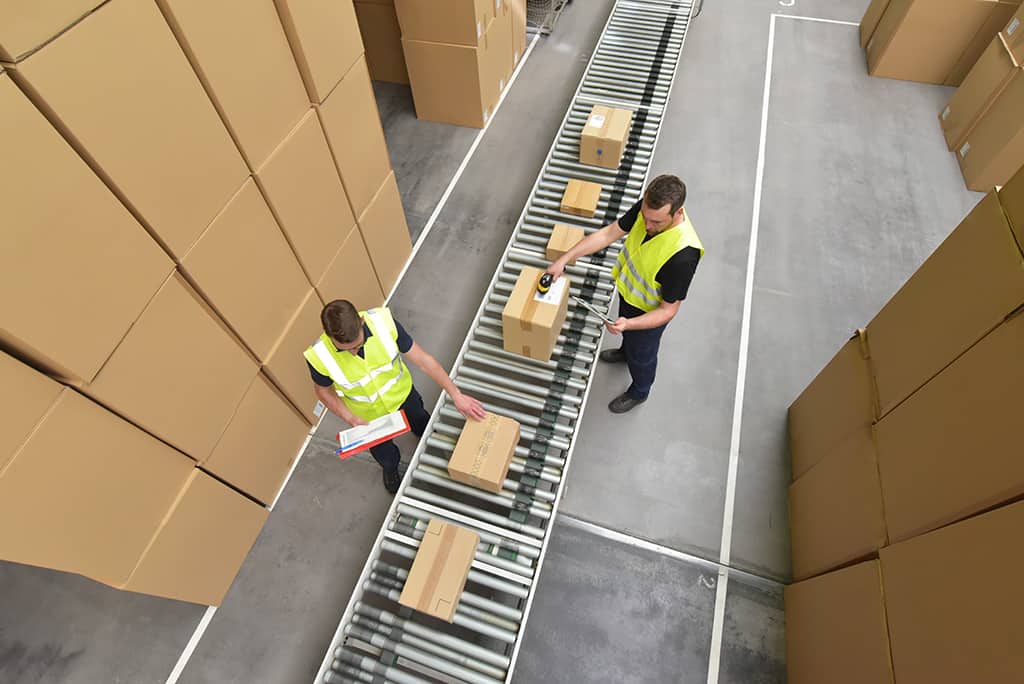

Shipping
The outbound dock or shipping station is responsible for shipping orders to the end customer. Outbound warehouse staff check shipping labels and place boxes in bays for FedEx, UPS, USPS, and other carriers. Shipping staff oversees the handoff from fulfillment to the delivery company.
Most 3PL companies work with multiple carriers, so you can choose the shipping methods that provide the customer experience your shoppers expect.
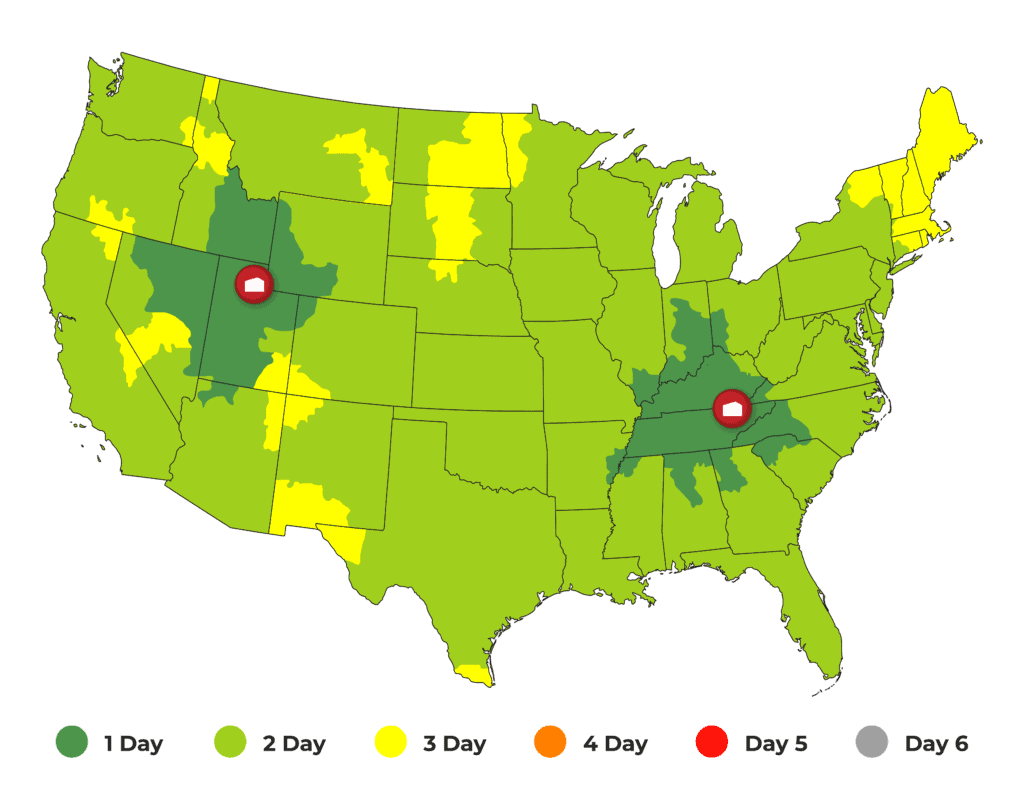
Warehouse location is a critical factor in the shipping process because shipping from the edges of the continental U.S. can take longer and cost more than shipping from centrally located warehouses. Choose a third-party fulfillment partner with warehouse locations that can ship to all or most of your customer base in two days or less.

Returns processing
Returns are unavoidable in online shopping, so your returns process is integral to your fulfillment strategy.
There are several ways to process returns:
- Have them shipped to your headquarters, even if you use a fulfillment center to ship orders.
- Provide refunds to your customers, but don’t ask them to send back unwanted merchandise.
- Use your fulfillment partner to process returns.
- Use a reverse logistics warehouse for returns.
Some ecommerce stores prefer to receive returns in-house to evaluate the condition of each returned item. That’s also helpful for returns due to manufacturing defects because you can send items directly to the factory for a refund of your costs.
For small or low-value items where return shipping might be greater than the cost of the product, the best returns practice is to give refunds and skip the return shipping and processing.
However, most online orders go back to a fulfillment warehouse. Having the 3PL that shipped the order process the return makes sense because the workers are familiar with your products and know how to handle them. Some ecommerce warehouses can examine returned goods, separating damaged or defective merchandise from merely unwanted stock. They can return like-new items to inventory to be sold again and send you photos so you have a record of the condition of returned products.
Warehouses specializing in returns can be chaotic because, unlike a fulfillment warehouse where most inventory comes with advance notice, warehouse staff has to manage an unpredictable inventory flow.
For items that can’t be sold as new, some brands create a line of seconds to recoup costs on returns. Other options are donating merchandise to charities or sending goods to the dump.
Customizing your ecommerce fulfillment
Different products need different fulfillment options. Shipping oversized or heavy items like bicycles or furniture differs from order processing for lightweight goods like apparel or accessories. If you sell high-value items, your customers may have expectations of faster shipping times and premium options. Small businesses need different logistics than large enterprises.
So, you need to customize your fulfillment to fit your ecommerce company. Here are some of the options to consider.

Shipping Options
Shipping options significantly affect customer experience at checkout in your online store. You should provide at least three choices, including standard and expedited shipping. Standard shipping is the lowest-cost (or free) choice and has the longest delivery times (but not too long). Expedited shipping is essential for customers who need an online order quickly.
Free shipping is a terrific way to incentivize purchases and keep customers returning to your site. If you can’t offer free shipping all the time without impacting your bottom line, you can still offer this perk.
- Give customers free shipping when they order above a certain dollar amount.
- Use free shipping as a limited-time promotion.
- Make free shipping a perk for high-value customers or those who join a loyalty club.

Ecommerce fulfillment options
There are a variety of ways to handle ecommerce fulfillment. Many online businesses use different methods at different times in their growth, and some use multiple fulfillment options at the same time.
In-house fulfillment
Many ecommerce companies, especially those that start small and bootstrap growth, begin with in-house fulfillment. In-house fulfillment can mean anything from packing orders in a spare bedroom to renting your own warehouse.
In-house fulfillment gives you total control over picking and packing your orders so you can ensure the quality meets your standards. You can add custom touches, such as a thank you note, a coupon, marketing materials, or a free gift.
However, self-fulfillment becomes increasingly challenging as your brand grows. In addition to all the other things you do to run your business, you have the task of hiring, training, and managing warehouse staff. And, when you rent your own space, you may pay for empty shelves during a slow period or end up short on space during peak times. Larger companies, even major brands, find value in outsourcing their fulfillment.
Outsourced order fulfillment
Outsourcing your fulfillment to a 3PL is like adding a new, expert team to your company overnight. You benefit from the experience of logistics professionals who work with many companies and can help you improve your order processing operations.
When you work with an excellent 3PL, your ecommerce order fulfillment happens automatically, freeing your time to focus on product development and marketing. When companies partner with the right 3PL for their brands, they often find their business growth accelerates.
Amazon FBA
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is an ecommerce fulfillment service that gives you access to Amazon’s vast logistics network. FBA ships orders from Amazon Marketplace, as well as other ecommerce platforms, and many sellers find it convenient to have sales and fulfillment on the same platform.
Using Amazon FBA gives you access to Amazon Prime shipping, but it has downsides for many businesses. FBA warehouses limit space, particularly during peak selling seasons, and the service, once marketed as a small business solution, requires a minimum sales velocity that smaller vendors can’t always meet. In addition, FBA doesn’t ship oversized or bulky products, and sellers complain about customer support issues when problems arise.
Hybrid fulfillment
Many ecommerce stores use a hybrid fulfillment model, shipping orders from multiple providers. The most common hybrid arrangement uses Amazon FBA plus in-house fulfillment or another fulfillment center for ecommerce stores. FBA provides benefits that brands selling on Amazon want and need, but it often limits warehouse space, particularly during peak season. A hybrid fulfillment solution gives you flexibility and keeps your orders flowing when you can’t restock FBA.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping allows you to sell products with less investment at the beginning. One trade-off for this reduced risk is less control over the fulfillment process. In addition, your profits on each sale will be lower.
Here’s how dropshipping works:
- You place items from a dropshipping manufacturer in your online store. You don’t buy any inventory until you make a sale.
- When you receive an order, you relay it to the manufacturer.
- The manufacturer ships orders directly to your customers; you never own the merchandise you sell. That is the essence of drop shipping.
- You split the profits with the manufacturer, so your cut is less when you dropship than when you maintain your own inventory.
The dropshipping business model is appealing if you want to start an online store with a minimal initial investment. For some entrepreneurs, dropshipping is a way to get started in ecommerce before moving on to a more traditional business model with more control over fulfillment and product quality.

Technology integrations
Integrations are a critical element of your fulfillment operations. A seamless link between your WMS and your ecommerce platform ensures that orders get to your warehouse for fast fulfillment and warehouse inventory data transfers back to your systems.
When you work with a 3PL, you have several integration options:
- Plugin. A plugin is a fast, easy, direct connection between an eCommerce platform like Shopify and your 3PL’s WMS. There’s no cost and no programming required.
- Middleware. Software that connects eCommerce software to a WMS is called middleware. A middleware connection requires no programming, but you will pay a monthly licensing fee to the middleware provider and won’t be able to customize your link.
- API. A custom connection or API has no ongoing costs, but plan on development costs and time upfront. API to WMS connections have the benefit of providing fast data transfer and being tailored to your business.
Planning your technology integrations is critical to getting set up with a new 3PL so you don’t have unnecessary delays. You need to connect your fulfillment warehouse to all your sales channels so that you can provide an omnichannel customer experience.

Kitting
Kitting groups multiple products or SKUs into a single package under a new SKU. You can use kitting to prepare subscription boxes, bulk orders, and gift sets, or simply group items your customers commonly order together.
Pre-kitting makes picking faster and more efficient. Not all warehouses offer this service, but Red Stag Fulfillment sees it as a core part of our mission because it greatly benefits our clients.
Benefits of outsourcing ecommerce fulfillment
Outsourcing your ecommerce order fulfillment is an economical way to meet your business needs as you grow and expand. Here are just a few of the ways a 3PL can help your brand.
Focus on other areas of your business
Well-executed order fulfillment is essential to online retail success, but it’s not a top skill for most ecommerce entrepreneurs. When you outsource your logistics, you outsource the headaches and the hard labor, giving you more time to focus on the parts of your business where you excel.
Leave logistical questions to experts
When you work with logistics professionals, you get the benefit of experience. Warehouse staff know how to handle your merchandise to prevent shrinkage and properly pack your orders for a delightful customer experience.

Reduced shipping costs
Ecommerce warehouses are high-volume shippers, so they may be able to negotiate lower shipping rates and pass discounts on to you. Plus, professionals can provide expert guidance and offer new solutions, such as package consolidation, to save you money on shipping.
Warehouse networks
In-house shipping is often limited to your business headquarters location, which may not be an ideal place for two-day order delivery. When you work with a 3PL, you can choose the best warehouse locations to reach your customers, placing your products in one or more warehouses to expand your reach.
Choosing an ecommerce fulfillment partner
There is no single best fulfillment company in the U.S. The best order fulfillment provider for your online store is one that meets all your logistics needs. Here are five things to look for in a fulfillment company.
Fulfillment center locations
Choose a 3PL with warehouse locations for national fulfillment so that you can ship to customers across the U.S.
Types of products
If you sell crock pots, your products won’t do well in a warehouse focused on apparel. Choose an ecommerce fulfillment provider with the experience and equipment to handle products and orders similar to yours. Ask about the typical package weight the warehouse ships and choose a 3PL that processes orders similar to yours.
Order volume
Some 3PLs require a minimum order volume, while others don’t. Your best fit is a warehouse working with clients that have a similar monthly order volume to your company, whether that’s in the hundreds or the thousands.
SKU count
There are warehouses that specialize in handling brands with high SKU counts and others that limit the number of SKUs they will stock for you. Your ideal 3PL will be in your SKU sweet spot.
Inventory shrinkage allowance
Inventory shrinkage is the industry term for inventory loss due to theft, damage, or simply being misplaced. Most 3PLs have a shrinkage allowance, which means you have to pay for a certain percentage of inventory loss. That can take a bite out of your bottom line, so choose a 3PL like Red Stag Fulfillment with a zero shrinkage policy. If Red Stag loses or damages an item, we pay the replacement cost.
How can ecommerce fulfillment fuel your brand’s success?
When it’s done well, ecommerce fulfillment is nearly invisible to your customers. Their orders arrive on time and are perfectly picked and packed, and they know that your brand is reliable and trustworthy, so they’ll order from you again. And again. That’s how online order fulfillment provides a solid foundation to build an ecommerce brand.
If you’re ready for industry-leading ecommerce fulfillment services, give Red Stag Fulfillment a call. We don’t just ship orders—we support growing companies.

Ecommerce fulfillment FAQs:
What is a fulfillment partner?
A fulfillment partner is a third-party logistics company (3PL) that processes orders for multiple eCommerce companies. Online retailers of all sizes turn to fulfillment providers for professional, expert eCommerce fulfillment.
Should I use an ecommerce fulfillment provider?
Many ecommerce companies benefit from using a fulfillment company. Outsourced fulfillment gives you professional order processing without hiring and training staff and flexible warehouse space without signing a lease. Partnering with a 3PL adds a whole new team that can help your company thrive.
How much does ecommerce fulfillment cost?
Each 3PL has its own ecommerce fulfillment pricing structure, and costs can vary based on the size of your typical package, your monthly order volume, and how much inventory you have in the warehouse. Typical fulfillment expenses include pick and pack fees (per order and item), box costs, shipping charges, and storage fees. Some 3PLs have a monthly fee for clients that don’t ship a minimum number of orders, and you might pay a fee for using more than one warehouse. Additional services, such as kitting and barcoding, are an added cost.
What is the difference between ecommerce and fulfillment?
Ecommerce is marketing consumer goods online and shipping them to customers. Fulfillment is the process of packing and shipping ecommerce orders. Fulfillment is a crucial part of ecommerce.
What is the difference between fulfillment and shipping?
Fulfillment is the process of storing merchandise and picking and packing orders. Shipping is sending orders to customers. A fulfillment warehouse prepares packages for shipping and then hands orders off to a delivery company to take to the end customer.










